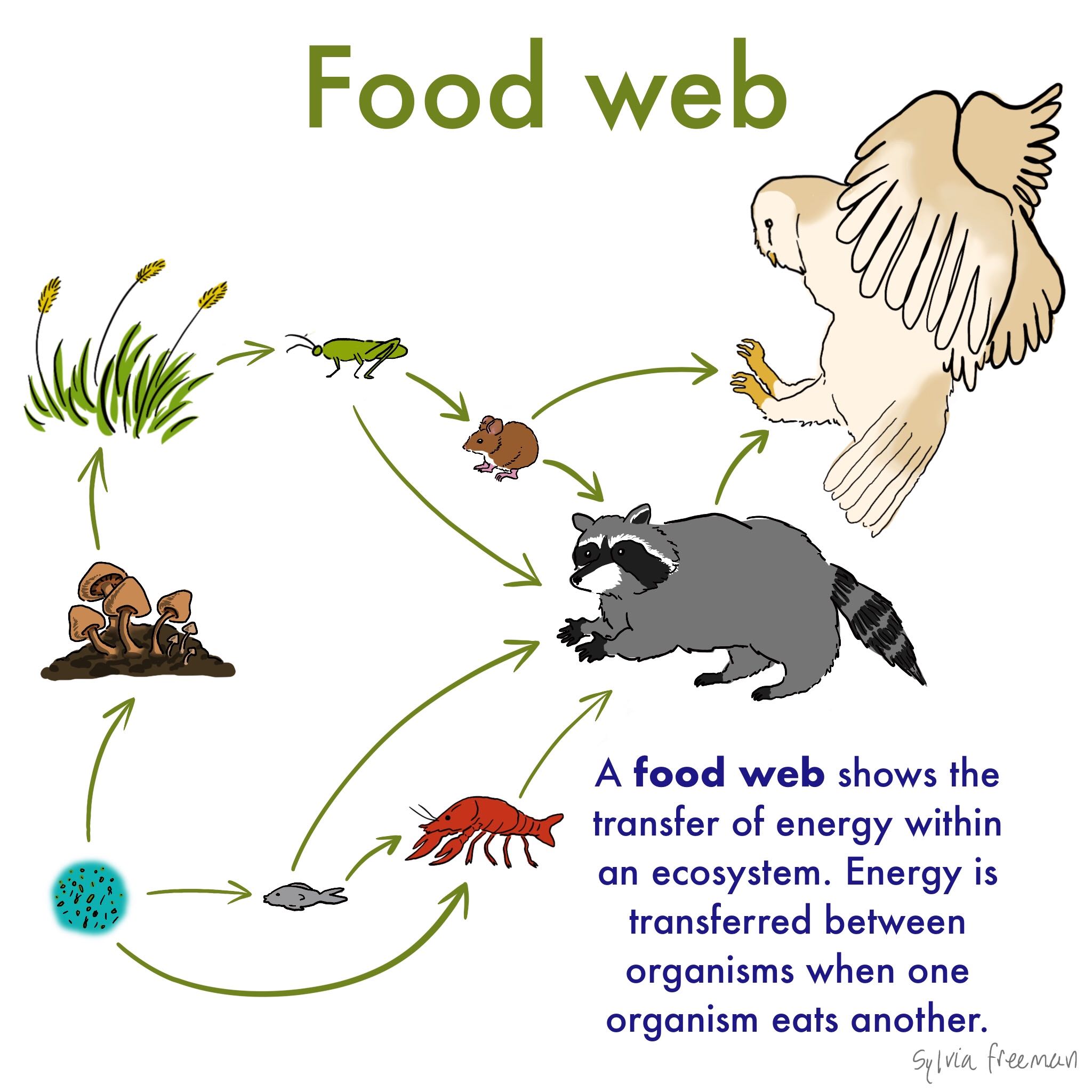
Where Is Plants In The Food Web . to represent these relationships more accurately, we can use a food web, a graph that shows all the trophic—eating. a food starts at trophic level 1 with primary producers such as plants, can move to herbivores at level 2, carnivores at level. These types of interactions occur between producer and. a food is a detailed interconnecting diagram that shows the overall food relationships between organisms in a particular. food web, a complex network of interconnecting and overlapping food chains showing feeding relationships within a community. a food incorporates different food chains within an environment. the linkages in a food illustrate the feeding pathways, such as where heterotrophs obtain organic matter by feeding on autotrophs and other. all species in the food webs can be distinguished into basal species (autotrophs, such as plants), intermediate species (herbivores and.
from www.expii.com
food web, a complex network of interconnecting and overlapping food chains showing feeding relationships within a community. These types of interactions occur between producer and. all species in the food webs can be distinguished into basal species (autotrophs, such as plants), intermediate species (herbivores and. to represent these relationships more accurately, we can use a food web, a graph that shows all the trophic—eating. a food is a detailed interconnecting diagram that shows the overall food relationships between organisms in a particular. a food incorporates different food chains within an environment. a food starts at trophic level 1 with primary producers such as plants, can move to herbivores at level 2, carnivores at level. the linkages in a food illustrate the feeding pathways, such as where heterotrophs obtain organic matter by feeding on autotrophs and other.
Food — Definition & Examples Expii
Where Is Plants In The Food Web a food incorporates different food chains within an environment. These types of interactions occur between producer and. a food incorporates different food chains within an environment. the linkages in a food illustrate the feeding pathways, such as where heterotrophs obtain organic matter by feeding on autotrophs and other. food web, a complex network of interconnecting and overlapping food chains showing feeding relationships within a community. all species in the food webs can be distinguished into basal species (autotrophs, such as plants), intermediate species (herbivores and. to represent these relationships more accurately, we can use a food web, a graph that shows all the trophic—eating. a food is a detailed interconnecting diagram that shows the overall food relationships between organisms in a particular. a food starts at trophic level 1 with primary producers such as plants, can move to herbivores at level 2, carnivores at level.
From bazaabigaillangdon.blogspot.com
What is a Food Abigail Langdon Where Is Plants In The Food Web These types of interactions occur between producer and. to represent these relationships more accurately, we can use a food web, a graph that shows all the trophic—eating. food web, a complex network of interconnecting and overlapping food chains showing feeding relationships within a community. a food incorporates different food chains within an environment. the linkages. Where Is Plants In The Food Web.
From wallpapercave.com
Food Webs Wallpapers Wallpaper Cave Where Is Plants In The Food Web the linkages in a food illustrate the feeding pathways, such as where heterotrophs obtain organic matter by feeding on autotrophs and other. a food incorporates different food chains within an environment. a food is a detailed interconnecting diagram that shows the overall food relationships between organisms in a particular. These types of interactions occur. Where Is Plants In The Food Web.
From nexusnewsfeed.com
What food webs tell us about our environment Nexus Newsfeed Where Is Plants In The Food Web These types of interactions occur between producer and. a food incorporates different food chains within an environment. the linkages in a food illustrate the feeding pathways, such as where heterotrophs obtain organic matter by feeding on autotrophs and other. food web, a complex network of interconnecting and overlapping food chains showing feeding relationships within a. Where Is Plants In The Food Web.
From vhmsscience.weebly.com
Food Webs Vista Heights 8th Grade Science Where Is Plants In The Food Web a food incorporates different food chains within an environment. a food is a detailed interconnecting diagram that shows the overall food relationships between organisms in a particular. a food starts at trophic level 1 with primary producers such as plants, can move to herbivores at level 2, carnivores at level. to represent these. Where Is Plants In The Food Web.
From swampbiologyproject.weebly.com
Food Freshwater Swamps Where Is Plants In The Food Web food web, a complex network of interconnecting and overlapping food chains showing feeding relationships within a community. the linkages in a food illustrate the feeding pathways, such as where heterotrophs obtain organic matter by feeding on autotrophs and other. to represent these relationships more accurately, we can use a food web, a graph that shows all. Where Is Plants In The Food Web.
From www.teachoo.com
Food Chain and Food Meaning, Diagrams, Examples Teachoo Where Is Plants In The Food Web These types of interactions occur between producer and. all species in the food webs can be distinguished into basal species (autotrophs, such as plants), intermediate species (herbivores and. to represent these relationships more accurately, we can use a food web, a graph that shows all the trophic—eating. food web, a complex network of interconnecting and overlapping food. Where Is Plants In The Food Web.
From freshwaterswampsinfo.weebly.com
Food Where Is Plants In The Food Web food web, a complex network of interconnecting and overlapping food chains showing feeding relationships within a community. to represent these relationships more accurately, we can use a food web, a graph that shows all the trophic—eating. a food starts at trophic level 1 with primary producers such as plants, can move to herbivores at level 2,. Where Is Plants In The Food Web.
From www231.pair.com
Food Webs Where Is Plants In The Food Web to represent these relationships more accurately, we can use a food web, a graph that shows all the trophic—eating. a food is a detailed interconnecting diagram that shows the overall food relationships between organisms in a particular. food web, a complex network of interconnecting and overlapping food chains showing feeding relationships within a community. all. Where Is Plants In The Food Web.
From asianbiomes.weebly.com
Food Webs Asian Biomes Where Is Plants In The Food Web to represent these relationships more accurately, we can use a food web, a graph that shows all the trophic—eating. the linkages in a food illustrate the feeding pathways, such as where heterotrophs obtain organic matter by feeding on autotrophs and other. a food incorporates different food chains within an environment. a food is. Where Is Plants In The Food Web.
From examples.yourdictionary.com
Simple Food Examples for Kids Where Is Plants In The Food Web a food is a detailed interconnecting diagram that shows the overall food relationships between organisms in a particular. a food incorporates different food chains within an environment. the linkages in a food illustrate the feeding pathways, such as where heterotrophs obtain organic matter by feeding on autotrophs and other. all species in the. Where Is Plants In The Food Web.
From www.dkfindout.com
What Is A Food Food Webs For Kids DK Find Out Where Is Plants In The Food Web a food starts at trophic level 1 with primary producers such as plants, can move to herbivores at level 2, carnivores at level. a food is a detailed interconnecting diagram that shows the overall food relationships between organisms in a particular. to represent these relationships more accurately, we can use a food web, a graph. Where Is Plants In The Food Web.
From www.worldatlas.com
Why Is Biodiversity Critical To Life On Earth? WorldAtlas Where Is Plants In The Food Web food web, a complex network of interconnecting and overlapping food chains showing feeding relationships within a community. a food is a detailed interconnecting diagram that shows the overall food relationships between organisms in a particular. These types of interactions occur between producer and. a food starts at trophic level 1 with primary producers such as. Where Is Plants In The Food Web.
From tropicalrainfoestblog.blogspot.com
Tropical rain forest travel Blog Day 4 food and pyramid Where Is Plants In The Food Web a food is a detailed interconnecting diagram that shows the overall food relationships between organisms in a particular. a food incorporates different food chains within an environment. to represent these relationships more accurately, we can use a food web, a graph that shows all the trophic—eating. These types of interactions occur between producer and. Web. Where Is Plants In The Food Web.
From wildsavannah.weebly.com
foodinteraction with explanation Savanna Where Is Plants In The Food Web a food incorporates different food chains within an environment. These types of interactions occur between producer and. all species in the food webs can be distinguished into basal species (autotrophs, such as plants), intermediate species (herbivores and. a food is a detailed interconnecting diagram that shows the overall food relationships between organisms in a particular.. Where Is Plants In The Food Web.
From www.expii.com
Food — Definition & Examples Expii Where Is Plants In The Food Web a food starts at trophic level 1 with primary producers such as plants, can move to herbivores at level 2, carnivores at level. the linkages in a food illustrate the feeding pathways, such as where heterotrophs obtain organic matter by feeding on autotrophs and other. These types of interactions occur between producer and. food web,. Where Is Plants In The Food Web.
From animalia-life.club
Desert Ecosystems Food Where Is Plants In The Food Web to represent these relationships more accurately, we can use a food web, a graph that shows all the trophic—eating. a food is a detailed interconnecting diagram that shows the overall food relationships between organisms in a particular. a food starts at trophic level 1 with primary producers such as plants, can move to herbivores at. Where Is Plants In The Food Web.
From worksheetschooldavidson.z21.web.core.windows.net
Food Chain And Food Vocabulary Where Is Plants In The Food Web a food starts at trophic level 1 with primary producers such as plants, can move to herbivores at level 2, carnivores at level. a food is a detailed interconnecting diagram that shows the overall food relationships between organisms in a particular. food web, a complex network of interconnecting and overlapping food chains showing feeding relationships. Where Is Plants In The Food Web.
From learnbyblogging.com
Book Review "Teaming with Microbes A Gardener's Guide to the Soil Where Is Plants In The Food Web food web, a complex network of interconnecting and overlapping food chains showing feeding relationships within a community. a food starts at trophic level 1 with primary producers such as plants, can move to herbivores at level 2, carnivores at level. a food incorporates different food chains within an environment. a food is a. Where Is Plants In The Food Web.